|
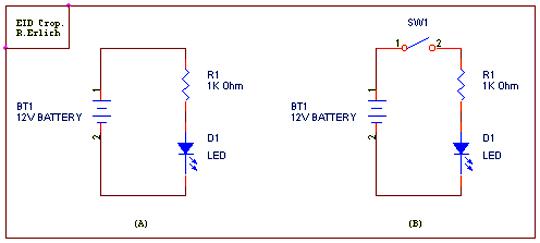
Calculating LED resistor connected to 12V Battery: LED current is typically around 10mA. When current flows throw the LED, electric voltage of about 1.6V will develop between its pins (between the LED's Anode and Cathode).
As connected in example (A) below, in order to calculate the resistor value, you need to subtract 1.6V from 12V and divide the result by 10mA (using Ohm's law) resulting in a value of 1040 Ohms. In this example, a resistor of 1K Ohms will suffice.
To select the resistor that suits your application, please visit EID's resistors page.
A switch can be added between the resistor and the battery so as to control the LED (see above drawing B). When the switch is closed, current flows and the LED light will be illuminated. In the open position, there is no current flow through the LED the LED will not be illuminated.
Note: If you change the battery to 6V battery the resistor value will change as follows: Using the formula R= (VBatt-VLED)/ILED, the new Resistor value is R=(6V-1.6V)/10mA=440 Ohms. In this instance, a resistor of 560 or 680 Ohms will suffice.
Construction: Connect the LED's Cathode pin, usually the short pin, to the negative battery terminal. Connect the appropriate serial resistor between the LED's Anode, usually the long pin, to the positive terminal on the battery.
|
||||
|
Description and SKU# |
Price 1-10 |
10-100 |
100-1K |
Picture |
|
LED Green 1 3/4 EID-L-LED-GRN |
.30 |
.25 |
.15 |
|
|
LED Yellow 1 3/4 EID-L-LED-YLW |
.30 |
.25 |
.15 |
|
|
LED Red 1 3/4 EID-L-LED-RED |
.30 |
.25 |
.15 |
|
|
LED Holder Clip and Ring 1 3/4 EID-L-LED-CAR |
.30 |
.25 |
.15 |
|
|
Small LED Green EID-L-LED-SGN |
.30 |
.25 |
.15 |
|
|
Small LED Red EID-L-LED-SRD |
.30 |
.25 |
.15 |
|
|
Small LED Holder Clip EID-L-LED-CLP |
.30 |
.25 |
.15 |
|