|
POWER-AC3PNDC-15LD. Low Current Dual Output 15 & -15 Voltage DC power supply board/Regulator Interface board with step-down power transformer (110V/60HZ primary).
the POWER-AC3PNDC-15LD. is an Electronics board that allows you to connect 110VAC/60HZ on one side of the board and get dual low current regulated voltages, 15VDC and -15VDC on the other side. Every industrial application designer should have a few of these boards handy. The boards will allow you to easily power all your Industrial Op-Amp transducers. The Terminal Block TB connector is included and makes it easy to use.
The POWER-AC3PNDC-15LD. board is designed to convert low current high voltages AC to stabilize +/- 15V DC. If used properly, it will eliminate the need for expensive industrial power supplies, which would otherwise be needed to carry out the same task.
AC3PNDC-15LD is easy to install, setup and operate. If you want to professionally power your HVAC products, POWER-AC3PNDC-15LD offers the features you need. Mounted easily via tow 0.125" mounting holes.
The board is designed to attenuate, filter and regulate low current low voltage AC to stable +/-15V DC.
For our line of transformers click Here
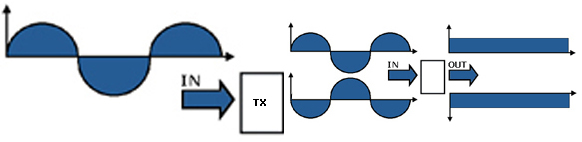
Standard Board 110VAC input (top) +/- 15V (bottom) Commonly utilized as the heart of DC Power Supply for Amplified and In-Line Amplified Transducer.
Basic operation of the voltage regulator board
Form the 110V AC the voltage drops to low dual AC voltages through the step down power transformer, the full diodes bridge D1-D4, together with the capacitor C1, C3 will convert input dual AC voltages to dual DC voltages.
The
other side of the diodes bridge drives the low current voltage regulators U1
and U2.
The voltage regulators are the main component of this regulators. The POWER-AC3PNDC-15C board typically has the ability to drive currents up to
80mA.
For maximum voltage regulation, adding capacitors C2 and C4
correspondingly in parallel between the common leg and the
output. This eliminates any high frequency AC
voltage that could otherwise combine with the output voltage.
|
||
|
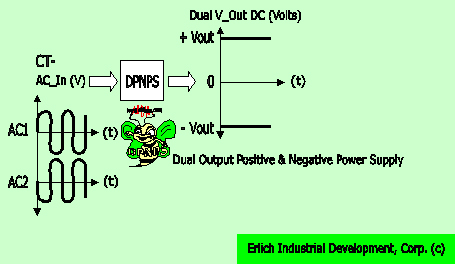
110VAC transformer convert to low voltage AC to low current -15VDC and +15VAC with common ground output
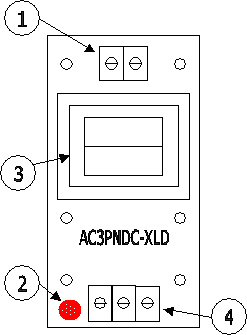
Figure A above shown model A (left) and B (right)
1. Input 110V/60Hz. 2. LED power indicator. 3. Isolated power transformer with CT. 4. Output +/- 15V DC.
|
||
|
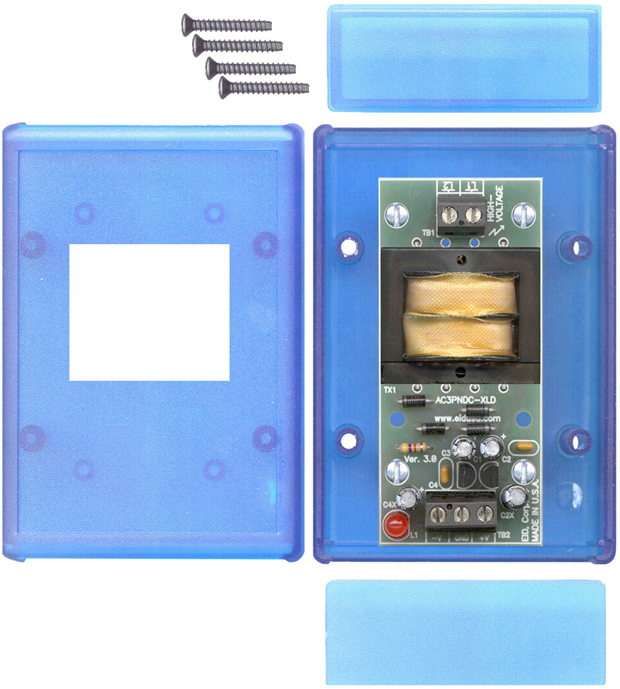
Mounting
Shown above mounted in plastic enclosure EID-1593 series enclosure (optional)
|
||
|
POWER-AC3PNDC-15LD Features
Specifications
|
||
|
Pricing
* Prices, P#, SKU# and colors are subject to change without notice.
|
||
|
Description and SKU# |
Price |
Picture |
|
15VDC and -15VDC PS Low current with step down transformer.
Input 110VAC, 60HZ, outputs +15V /80mA & -15V /80mA
P# EID-POWER-PSD-AC3PNDC15LD |
75.33 |
|
|
5VDC and -5VDC PS Low current with step down transformer.
Input 110VAC, 60HZ, outputs +5V /80mA & -5V /80mA
P# EID-POWER-PSD-AC3PNDC5LD |
97.92 |
|
|
Modified ABS Plastic Instrument enclosures option |
EID-1593LBK |
$7.97 |
|
Modified Translucent blue ABS Plastic Instrument enclosures option |
EID-1593LTBU |
$10.75 |
|
Din rail mounting mounting kit option |
EID-1427DINCLIP |
$4.242 |